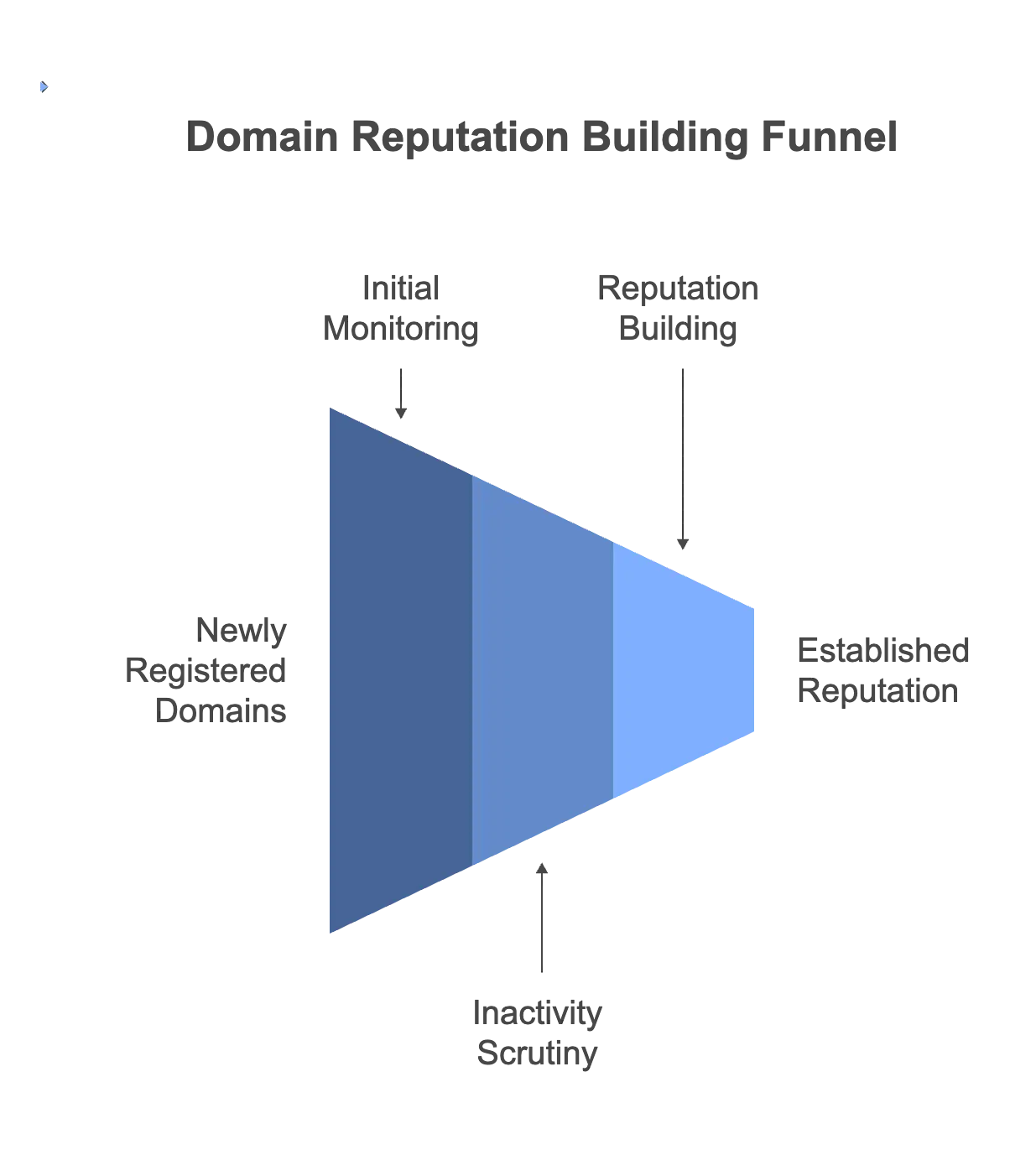
When is a domain considered new?
A domain is generally considered “new” if it has recently been registered or has had little to no email-sending history. Email service providers (ESPs) and internet service providers (ISPs) categorize domains as new based on factors like age, activity level, and sender reputation. Here’s what typically defines a new domain:
- Registration age: Most ESPs consider a domain “new” if it has been registered within the past 30-90 days. During this period, ESPs and ISPs closely monitor the domain’s activity to establish its sending behavior and reputation.
. - Sending history: Even if a domain is older, it can be treated as new if it has minimal or no email activity. Domains that begin sending emails suddenly after a long period of inactivity often undergo scrutiny similar to brand-new domains.
- Reputation building period: The domain is considered “new” until it establishes a sending reputation through consistent, high-quality email engagement and low spam complaints. This warmup period, during which the domain gradually builds credibility, typically spans several weeks to months.
In summary, a domain’s “new” status is based on recent registration, lack of email history, and unestablished reputation. For optimal results, new domains should undergo a warmup process to build credibility and ensure emails reach inboxes.
